
Understanding Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve, the nerve that sends signals from the eye to the brain. It is often linked to high pressure in the eye, which can lead to vision loss if not treated. Vision loss from glaucoma is permanent and irreversible.
The Silent Thief of Sight
Often called the “Silent Thief of Sight” Glaucoma does not have obvious symptoms. Because vision loss starts at the edge of the field of vision and progresses inwards slowly, by the time it is noticeable it is often too late.
Some forms of glaucoma even occur within normal eye pressure ranges, making it difficult to catch. Because of this, routine examination from a trained professional is vital for early detection and treatment.
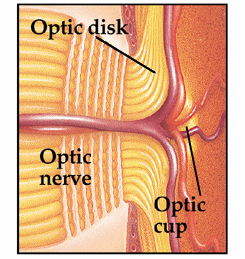
Healthy Optic Nerve
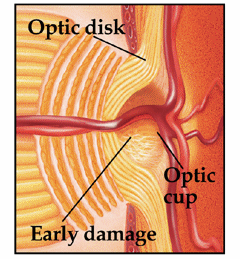
Early Damage
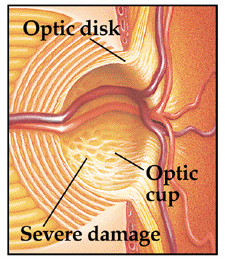
Advanced Glaucoma Damage
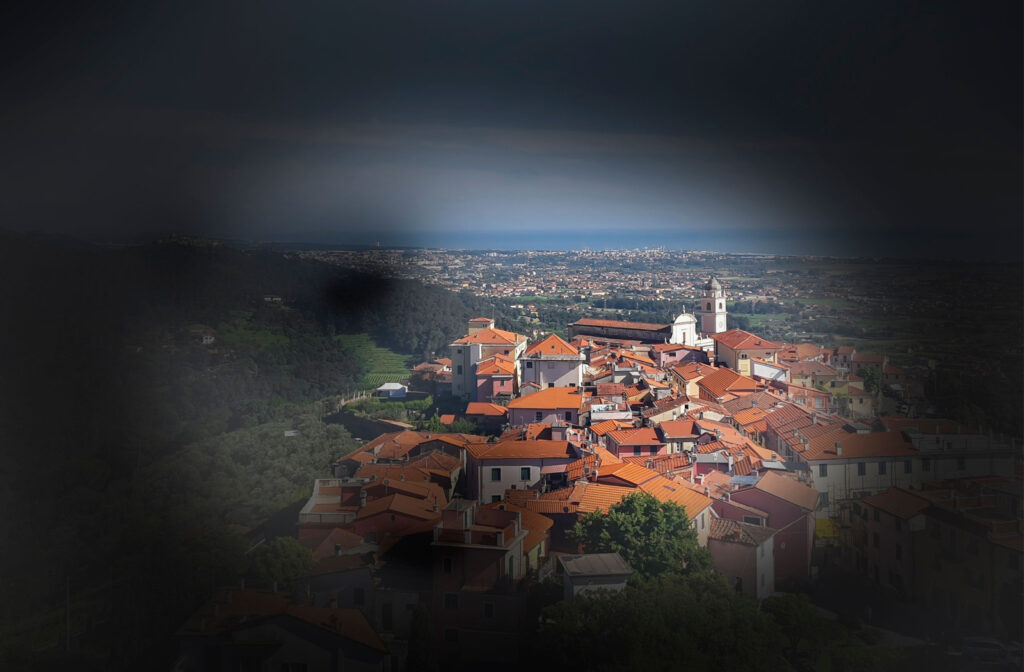

Advanced Vision Loss from Glaucoma Damage
How is Glaucoma Diagnosed?
Glaucoma is diagnosed through a comprehensive eye exam, including:
- Eye Pressure Test (Tonometry): Measures the pressure inside your eye
- Optic Nerve Inspection: A doctor will examine the optic nerve for signs of damage
- Visual Field Test: Checks for vision loss in the peripheral areas
- Pachymetry: Measures the thickness of the cornea, which can affect eye pressure readings
Who is at Risk?
- Age (60 and older)
- Family history of glaucoma
- African, Hispanic, or Asian descent
- High eye pressure
- Medical conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure
- Eye injuries or long-term use of corticosteroid medications


